

The telescopic shock absorber is a part of the suspension system that is used as a spring device to achieve a compromise between flexibility and stiffness. It absorbs the shock energy converted into the vertical movement of the shaft, providing cushioning and dissipating it into heat.
Table of Contents
Purpose of telescopic shock absorber
- To control vibrations in the springs.
- To provide a comfortable ride.
- Act flexible and be rigid enough.
- To resist unnecessary spring movement.
- It is used to absorb shocks that occur while driving on uneven roads.
- It is also used for vehicle stability under sudden acceleration or braking conditions.
Construction of Telescopic shock absorber
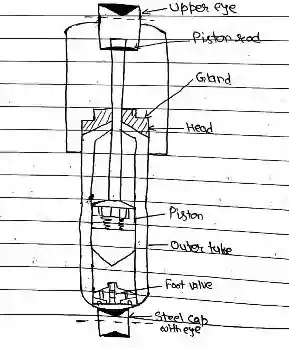

- It consist of a cylinder to which head is welded. The head is screwed into the top end of the outer tube.
- To the bottom end of the outer tube is welded pressed Steel cap and eye or ring. This eye is connected to wheel axle.
- The Piston slides inside the cylinder. This piston is secured to the piston rod which at its upper end has an eyes welded to it with this eye, the piston rod is attached to the frame of the vehicle the outside part of the piston rod is protected by a dust shield which is welded to the fixing eyes.
- A gland prevents oil leakage from where the piston rod passes through the head.
- The gland consists of a piston rod, Oil seal, Oil seal gasket, seal retainer, Oil seal spring and Oil seal cup. Any fluid scraped off by the gland packing passes down a drain hole to the reservoir space between the cylinder and outer tube.
- The Piston has two concentric rings of holes drilled through it. The outer ring of hole is covered at the top by a disc valve which is held down by a star shape disc spring.
- The inner ring hole is covered by disc valve from bottom by the coil spring. There is a foot valve assembly at the bottom of the cylinder. The foot valve assembly is similar to that piston assembly, except that the lower disc valve which covers the inner ring of holes is held up by a disc valve spring instead of coil spring. Both ends of the cylinder are completely filled by a mixture of 60% transformer oil and 40% turbine oil and the space between the tube and cylinder.
Working of Telescopic shock absorber
- When a vehicle come across the bump, the bottom eyes is moved upwards, then the fluid below the piston must be displaced to the top side of the piston.
- The fluid will now pass through the outer ring of hole in the piston by lifting the top disc against the disc spring. But the volume above the piston is less due to piston rod.
- As such, fluid from the bottom of the piston will also get displaced through inner ring of holes in the foot valve and enter the reservoir space between the cylinder and Outer tube. So the fluid level in the reservoir space will rise.
- The pressure set up in the system will depend upon the size of the passage open by valve in the Piston and foot valve. This will depend on the square of the speed at which the cylinder is moved upward.
- When the cylinder moves downward, fluid will be displaced from the upper end of the cylinder to lower end through the inner ring of hole in the piston by opening the lower disc valve against coil spring. Because of the volume of the piston rod that leaves the cylinder, the fluid will be drawn into the lower end of the cylinder from the reservoir space through the outer ring of hole in the foot valve. This passing of fluid through opening provide damping.
Advantages of the telescopic shock absorber
- Noise-free operation
- Less maintenance required.
- Safer machine operation
- Low manufacturing cost.
- High speed of operation.
- Longer machine life
- Higher operating speeds
Disadvantages of Telescopic shock absorber
- It has a low ability to resist environmental pollution and temperature change.
- It is difficult for a damper to reach the natural frequency.
- Some types cannot be repaired but must be replaced.
Types of shock absorbers
- Mechanical damper (friction type)
- Hydraulic shock absorber.
Twin-tube shock absorber
It is the type of shock absorber in which 2 hollow tubes are used called the primary tube and the secondary tube or shell that are merged in a telescope shape, that is, the primary tube inside the secondary tube or shell.
The primary tube contains the moving piston, compression valve along with other assembly components and is filled with high viscosity index oil.
The secondary tube or shell contains the primary tube together with low pressure gas (mainly nitrogen gas).
This entire double-tube assembly is surrounded by a coil spring that provides stiffness and also helps this assembly return to its initial position after actuation.
Monotube shock absorber


It is the type of shock absorber in which instead of a double tube, a single tube is used inside which the mobile piston is placed.
High viscosity index oil along with low pressure gas (nitrogen in most cases) is filled inside a single tube in a particular ratio.
The oil and gas filled within this single tube are separated by a floating piston that is sealed inside the tube.
This entire assembly is surrounded by a coil spring just like a two-tube shock absorber.
Advantages of the Mono-shock suspension system
- The monoshock suspension system improves the motorcycle’s handling when going over bumps or rough roads as all the force is concentrated at one point.
- Because the monoshock suspension position is positioned ahead of the rear axle in the center of the motorcycle, swingarm motion is not transferred directly to the suspension, allowing for greater stability.
- The performance of the motorcycle is more constant than the use of double shock absorber.
- More elegant suspension system.
Monotube gas filled shock absorbers
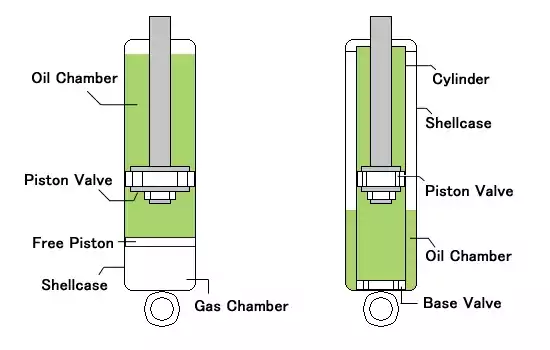

To prevent foaming and bubbling of the oil, which degrades shock performance, a gas-filled monotube shock has a high-pressure nitrogen chamber above the oil chamber. This high-pressure gas makes it difficult for the oil to bubble up, even when the shock is moving in and out very quickly, as might happen when traveling fast on a very rough road or like a washboard.
Gas-filled shocks are expensive as they require tight manufacturing tolerances, but they are very resistant to fading and consequently are popular in off-road racing and rallying. Gas-filled shocks, by the way, are not the same thing as “air shocks,” which use an air chamber separate from the shock oil. An air spring is actually an air chamber that raises or lowers the vehicle when air is added or removed through a valve.
Advantages of gas filled shock absorber
- The full diameter of the tube can be used as the working chamber, thus making a larger volume of oil available for damping.
- The largest volume of oil available in any stroke due to adjustments between gas and oil volumes provides better ease of damping force.
- Heat tolerance in gas filled shock absorber is higher.
- Gas-filled shock absorber extends the life of tires and other suspension related components, such as springs, brushes, etc.
- A gas-filled shock absorber is designed to reduce oil foaming.
- Provide stability while grading turns.
Which suspension is better – Telescopic or Hydraulic
Telescopic Suspension:
Telescopic suspension usually refers to the design of shock absorbers or struts. Shock absorbers are commonly used in various vehicle types. They consist of a piston that moves within a cylindrical tube filled with hydraulic fluid. As the suspension moves, the piston compresses the hydraulic fluid, providing damping to control the motion of the vehicle.
Hydraulic Suspension:
On the other hand, hydraulic suspension refers to the use of hydraulic fluid in the suspension system. Hydraulic fluid is often used in shock absorbers to provide damping, but it can also be used in other components of the suspension system.
FAQ
Is telescopic suspension good?
Telescopic suspension is mainly used for motorcycles, where it is very successful due to its weight and absorption capacity. The main purpose of the suspension is to resist unnecessary spring movement and provide a very comfortable ride. It also provides stability while graduating.
What are the three types of shock absorbers?
Hydraulic type shock absorbers. Double effect shock absorbers. Single effect shock absorber.
What is telescopic shock absorber?
A telescopic shock absorber can be compressed and extended; the so-called slam slam and rebound slam. Telescopic shock absorbers can be subdivided into: Twin-tube or twin-tube shock absorbers, available in hydraulic and gas-hydraulic configuration. Monotube shock absorbers, also called high pressure gas shock absorbers.
How many eyes do telescopic shock absorbers have?
Two eyes
- Mechanical damper (friction type)
- Hydraulic shock absorber.
You may also like

[…] Telescopic shock absorber […]
Thanks mate
Saw you purpose for starting this and putting this much effort s
Appreciated 👍🏽