50-Interview Question and Answer on Directional Control Valve
What is a Directional Control Valve?
A directional control valve is a type of valve used to control the direction of fluid flow in a hydraulic or pneumatic system.
What are the main types of directional control valves?
The main types of directional control valves are spool valves, poppet valves, and rotary valves.
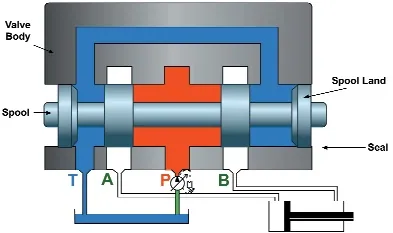
What is a spool valve?
A spool valve consists of a cylindrical spool that moves linearly inside a valve body to control the flow direction.
What is a poppet valve?
A poppet valve uses a disk or cone-shaped element that moves in and out of a seat to control the flow direction.
What is a rotary valve?
A rotary valve uses a rotating element to control the flow direction.
What are the common symbols used to represent directional control valves in hydraulic schematics?
Common symbols include arrows, rectangles, and triangles indicating the direction of flow and valve positions.
What is the purpose of a center position in a directional control valve?
The center position is used to stop fluid flow or to allow the fluid to return to a reservoir.
What is a 3/2-way valve?
A 3/2-way valve has three ports and two flow positions, usually labeled as “A,” “B,” and “P” (for the pressure or pump port).
What is a 4/2-way valve?
A 4/2-way valve has four ports and two flow positions, typically labeled as “A,” “B,” “P,” and “T” (for the tank or reservoir port).
What is a 5/2-way valve?
A 5/2-way valve has five ports and two flow positions. It is commonly used in pneumatic systems.
What is a 5/3-way valve?
A 5/3-way valve has five ports and three flow positions. It is often used in pneumatic systems to control double-acting cylinders.
What is the difference between normally open (NO) and normally closed (NC) valves?
A normally open valve allows flow in its resting state and blocks flow when actuated. A normally closed valve blocks flow in its resting state and allows flow when actuated.
What is the difference between a direct-acting valve and a pilot-operated valve?
A direct-acting valve operates directly in response to an applied force, while a pilot-operated valve uses the force of a smaller control valve or pilot valve to operate the main valve.
What are the advantages of using a pilot-operated valve?
Pilot-operated valves can handle high pressures, have lower pressure drop, and require less force to actuate.
What are the advantages of using a solenoid-operated valve?
Solenoid-operated valves offer quick response times, precise control, and ease of automation.
What is the difference between a 2-position and a proportional directional control valve?
A 2-position valve has only two flow positions, whereas a proportional valve allows for variable control of flow rates.
What are some common applications of directional control valves?
Directional control valves are used in hydraulic and pneumatic systems, such as in mobile machinery, industrial equipment, and automation systems.
What factors should be considered when selecting a directional control valve?
Factors include the required flow rate, pressure rating, operating temperature, fluid compatibility, and the type of actuation required.
What is pressure drop in a directional control valve?
Pressure drop refers to the decrease in pressure across a valve when fluid flows through it. It depends on factors like valve design, flow rate, and fluid viscosity.
What is the purpose of a check valve in a directional control valve circuit?
A check valve allows flow in one direction while blocking flow in the opposite direction, preventing backflow and ensuring system stability.
What is the difference between a single-acting and a double-acting cylinder?
A single-acting cylinder has fluid pressure applied to only one side, providing force in one direction. A double-acting cylinder has fluid pressure applied to both sides, allowing force in both directions.
How is a sequence valve used in a hydraulic system?
A sequence valve is used to control the sequence of operations in a hydraulic system by ensuring that one actuator completes its stroke before another actuator begins.
What is a pressure relief valve?
A pressure relief valve is used to limit the maximum pressure in a hydraulic system by diverting excess fluid flow back to the reservoir.
How does a pressure-compensated flow control valve work?
A pressure-compensated flow control valve automatically adjusts the flow rate to maintain a constant flow, regardless of pressure variations in the system.
What is the difference between a spool-type and a poppet-type directional control valve?
A spool-type valve uses a sliding spool to control flow, while a poppet-type valve uses a poppet or ball to control flow.
What is a detent feature in a directional control valve?
A detent feature allows the valve to remain in a specific position even when there is no actuating force, providing stability and preventing unintended movement.
What is a load-holding valve, and how is it used?
A load-holding valve is used to hold the load in position when the actuator is not in operation, preventing unintentional movement.
What is a shuttle valve, and what is its purpose?
A shuttle valve allows flow from multiple sources and directs it to a common outlet, ensuring fluid supply from the available source with the highest pressure.
How is a counterbalance valve used in a hydraulic system?
A counterbalance valve is used to control the motion of a vertically mounted actuator to prevent it from falling due to gravity.
What is the difference between a monoblock valve and a sectional valve?
A monoblock valve is a compact valve block with all the necessary valves and functions integrated into a single unit. A sectional valve consists of individual valve sections that can be combined to create custom valve assemblies.
How is a flow divider valve used in a hydraulic system?
A flow divider valve divides a single input flow into two or more proportional output flows, ensuring equal distribution.
What is the purpose of an emergency stop valve in a pneumatic system?
An emergency stop valve is designed to quickly exhaust air from the system to stop motion or prevent damage in emergency situations.
What is a manual override feature in a directional control valve?
A manual override feature allows manual actuation of the valve, bypassing the automated control system.
What is the function of a speed control valve in a pneumatic system?
A speed control valve regulates the speed of an actuator by controlling the rate at which air exhausts from the cylinder.
What is the difference between a spool-and-sleeve valve and a poppet valve?
A spool-and-sleeve valve uses a cylindrical spool that slides within a sleeve, while a poppet valve uses a disk or cone-shaped element.
How does a pilot-operated check valve work?
A pilot-operated check valve allows free flow in one direction and blocks flow in the opposite direction unless pilot pressure is applied, opening the valve.
What is a 3-position valve?
A 3-position valve has three flow positions or modes of operation, typically referred to as A, B, and C.
How does a proportional pressure relief valve work?
A proportional pressure relief valve adjusts the pressure at the valve outlet based on an electrical or proportional control signal, providing precise pressure control.
What is a tandem center position in a directional control valve?
A tandem center position is a valve configuration where all ports are blocked in the center position, providing a neutral state for the actuator.
How does a pressure reducing valve function?
A pressure reducing valve maintains a constant reduced pressure downstream, regardless of fluctuations in the upstream pressure.
What is the difference between a closed-center and an open-center valve configuration?
In a closed-center configuration, all ports are blocked in the center position, while in an open-center configuration, flow is allowed through the center position when no actuation is applied.
How is a directional control valve actuated?
Directional control valves can be actuated manually, mechanically, pneumatically, electrically, or hydraulically, depending on the application and control requirements.
What is the purpose of a spool position indicator on a directional control valve?
A spool position indicator provides visual or electronic feedback on the current position of the spool, allowing the operator to know the valve’s status.
What is a latching valve, and how does it work?
A latching valve is designed to hold its position after being actuated until a signal is received to change its state. It uses mechanical or magnetic latching mechanisms.
How does a 4-way proportional directional control valve function?
A 4-way proportional valve controls both the direction and flow rate of the fluid by varying the current to a proportional solenoid, providing precise control over the actuator.
What is a needle valve, and where is it commonly used?
A needle valve is a type of flow control valve with a long, tapered needle-like plunger used for fine adjustment of flow rates. It is commonly used in pneumatic and hydraulic systems.
How does a shuttle valve differ from a check valve?
A shuttle valve allows flow from multiple sources to a common outlet, while a check valve only permits flow in one direction.
What is a spool overlap in a directional control valve?
Spool overlap refers to the period when two flow paths are open simultaneously during the transition of the spool from one position to another.
How does a hydraulic pilot-operated check valve work?
A hydraulic pilot-operated check valve allows flow in one direction and blocks flow in the opposite direction unless pilot pressure is applied, opening the valve.
What is the difference between a direct-acting and a pilot-operated solenoid valve?
A direct-acting solenoid valve operates the valve directly using an electromagnetic force, while a pilot-operated solenoid valve uses the solenoid to control a smaller pilot valve that, in turn, operates the main valve.
These questions cover a wide range of topics related to directional control valves, and they should provide a good foundation for an interview on the subject.
You may also like
