50 Interview questions answers on flow control valve
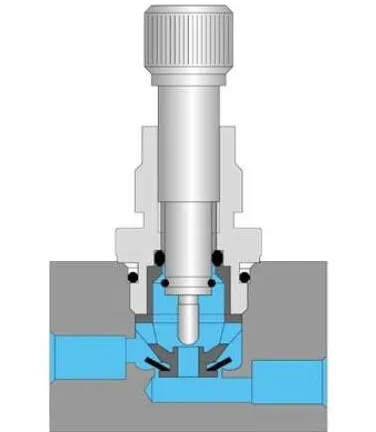
Q: What is a flow control valve?
A flow control valve is a device used to regulate or control the flow rate of a fluid in a system.
Q: What are the different types of flow control valves?
Some common types of flow control valves include needle valves, globe valves, ball valves, butterfly valves, and gate valves.
Q: What is the purpose of a flow control valve?
The main purpose of a flow control valve is to maintain a desired flow rate in a system by adjusting the opening or restriction of the valve.
Q: How does a flow control valve work?
Flow control valves work by creating resistance or obstruction in the flow path, which results in controlling the flow rate.
Q: What are the key components of a flow control valves?
The key components of a flow control valve include a valve body, a flow passage, a control element (such as a disc or needle), and an actuator.
Q: What are some common applications of flow control valves?
Flow control valves are commonly used in various industries, including oil and gas, chemical processing, water treatment, HVAC systems, and manufacturing processes.
50 Interview questions & answers on Flow Control Valve
Q: What factors should be considered when selecting a flow control valves?
Factors such as the required flow rate, pressure rating, temperature range, fluid compatibility, and system requirements should be considered when selecting a flow control valves.
Q: What is the difference between a flow control valve and a throttling valve?
The terms “flow control valve” and “throttling valve” are often used interchangeably to refer to valves used for flow regulation.
Q: How is the flow rate controlled in a flow control valve?
The flow rate is controlled by adjusting the position of the valve’s control element, which can vary the effective flow area.
Q: What are the advantages of using a flow control valves?
Some advantages of using flow control valves include precise flow regulation, increased system efficiency, protection against excessive flow, and the ability to balance flow in different branches of a system.
Q: What is cavitation in flow control valves?
Cavitation is the formation and collapse of vapor bubbles in a flowing liquid due to pressure variations, which can damage flow control valves and other system components.
Q: How can cavitation be prevented in flow control valves?
Cavitation can be prevented by selecting valves designed to handle the specific flow conditions, using materials resistant to cavitation damage, and employing proper valve sizing and pressure control.
Q: What is the purpose of the actuator in a flow control valve?
The actuator is responsible for positioning and operating the control element of the valve, allowing for manual or automated control of the flow rate.
Q: What are the different types of valve actuators?
Valve actuators can be pneumatic (air-operated), hydraulic (liquid-operated), electric, or manual (hand-operated).
Q: What is the function of the positioner in a flow control valve?
The positioner is a device used to precisely position the valve’s control element based on the input signal from a controller, ensuring accurate flow regulation.
50 Interview questions & answers on Flow Control Valve
Q: What is the significance of the flow characteristic in a flow control valve?
The flow characteristic determines how the flow rate changes in relation to the valve’s position. Common flow characteristics include linear, equal percentage, and quick opening.
Q: What is the importance of proper valve sizing in flow control applications?
Proper valve sizing is crucial to ensure the valve can handle the required flow rate and provide accurate control while minimizing pressure drop and potential issues like cavitation.
Q: How can pressure drop be minimized in flow control valves?
Pressure drop can be minimized by selecting valves with low flow resistance, using larger diameter valves, reducing the number of bends or restrictions in the flow path, and optimizing the system design.
Q: What is the role of the control signal in a flow control valve?
The control signal, such as a voltage, current, or pneumatic pressure, is used to modulate the position of the valve’s control element, thereby regulating the flow rate.
Q: What is the difference between an open-loop and closed-loop control system for flow control?
In an open-loop control system, the control signal is not based on feedback, while in a closed-loop control system, the control signal is adjusted based on feedback from sensors measuring the flow rate.
Q: How can flow control valves be protected against corrosion?
Flow control valves can be protected against corrosion by selecting appropriate corrosion-resistant materials, such as stainless steel or specialized coatings, and implementing proper maintenance practices.
Q: What are the potential safety considerations when working with flow control valves?
Safety considerations may include proper handling of hazardous fluids, adherence to industry regulations and standards, use of appropriate personal protective equipment, and ensuring valves are installed and operated correctly.
Q: How can flow control valves contribute to energy conservation in a system?
Flow control valves can help conserve energy by reducing excessive flow rates, minimizing pressure drop, and optimizing system performance to operate more efficiently.
Q: What is the effect of viscosity on flow control valves?
Higher viscosity fluids tend to require higher actuating forces and may affect the valve’s control response due to increased resistance to flow.
Q: How can leakage be minimized in flow control valves?
Leakage can be minimized by selecting valves with tight shutoff capabilities, proper installation techniques, regular maintenance, and periodic inspections.
Q: What are the advantages and disadvantages of using a manual flow control valves?
The advantages of manual flow control valves include simplicity, reliability, and lower cost. However, they lack the ability for automated control and remote operation.
50 Interview questions & answers on Flow Control Valve
Q: What are the advantages and disadvantages of using an electrically actuated flow control valves?
The advantages of electrically actuated flow control valves include precise control, automation capability, and the ability to integrate with control systems. However, they can be more expensive and require a power source.
Q: What is the importance of proper valve maintenance?
Proper valve maintenance is important to ensure the valve’s reliability, longevity, and optimal performance. It includes regular inspection, cleaning, lubrication, and repair or replacement of worn components.
Q: What are the key considerations for installing flow control valves?
Key considerations for installing flow control valves include proper orientation, alignment, support, and connection to the piping system. It is also important to follow the manufacturer’s installation guidelines.
Q: How can the flow rate be accurately measured in a system with flow control valves?
Flow rate can be accurately measured using flow meters, such as differential pressure meters, magnetic flow meters, ultrasonic flow meters, or turbine flow meters, installed in the system.
Q: What is the purpose of the flow coefficient (Cv) in flow control valves?
The flow coefficient represents the flow capacity of a valve for a given pressure drop. It is used to compare the flow capacities of different valves and assist in valve selection.
Q: Can flow control valves be used for both liquids and gases?
Yes, flow control valves can be used for both liquids and gases. However, specific valve designs and materials may be required based on the properties of the fluid being controlled.
Q: What is the impact of temperature on flow control valves?
Temperature can affect the performance and materials of flow control valves. High temperatures can cause expansion or damage to valve components, while low temperatures can lead to freezing or increased viscosity.
Q: How can flow control valves contribute to process optimization?
Flow control valves allow precise control of flow rates, enabling optimization of processes by maintaining desired conditions, minimizing waste, and enhancing overall system efficiency.
Q: What are the potential sources of flow control valve malfunction or failure?
Flow control valve malfunction or failure can be caused by factors such as improper installation, damage to internal components, wear and tear, contamination, or inadequate maintenance.
Q: What is the role of feedback control loops in flow control systems?
Feedback control loops use sensors to measure the flow rate and provide feedback to the control system, enabling adjustments to the flow control valve’s position to maintain the desired flow rate.
Q: Can flow control valves be used in hazardous or explosive environments?
Yes, flow control valves can be designed and certified for use in hazardous or explosive environments by incorporating safety features and following relevant industry standards.
Q: What are the considerations for selecting the appropriate actuator type for a flow control valves?
Considerations include the required actuating force, control signal type available, response time, environmental conditions, and compatibility with the control system.
Q: How can flow control valves be protected against excessive pressure?
Flow control valves can be protected against excessive pressure by incorporating pressure relief valves or using pressure regulators upstream or downstream of the valve.
Q: How can flow control valves be used in a proportional control system?
Flow control valves can be integrated into a proportional control system by adjusting the valve’s position proportionally to the control signal, enabling precise flow rate modulation.
Q: What are the differences between an on-off valve and a flow control valve?
An on-off valve is designed to either fully open or fully close the flow path, while a flow control valve provides continuous control over the flow rate by varying the valve’s position.
Q: What are the potential challenges associated with controlling flow in large-scale systems?
Challenges may include pressure drop considerations, maintaining uniform flow distribution, system balancing, control system design, and integration of multiple flow control valves.
50 Interview questions & answers on Flow Control Valve
Q: Can flow control valves be used for two-phase flow, such as steam-water mixtures?
Yes, flow control valves can be designed specifically for two-phase flow applications, considering the properties and behavior of the mixture, such as flow regime and critical flow conditions.
Q: What is the impact of flow control valve positioning accuracy on system performance?
Flow control valve positioning accuracy is crucial for maintaining the desired flow rate and overall system performance. Inaccurate positioning can result in flow deviations and affect process control.
Q: How can flow control valves be protected against external contaminants?
Flow control valves can be protected by using filters or strainers in the upstream flow path to remove solid particles or debris that could potentially damage or clog the valve.
Q: What are the considerations for selecting the appropriate flow control valve for a specific application?
Considerations include the required flow range, pressure and temperature ratings, fluid compatibility, control accuracy, response time, actuation method, and overall system requirements.
Q: How can flow control valves be calibrated or adjusted for accurate flow regulation?
Flow control valves can be calibrated or adjusted by following the manufacturer’s guidelines, using appropriate tools, and comparing the actual flow rate with the desired flow rate.
Q: What are the potential effects of system pressure fluctuations on flow control valve performance?
System pressure fluctuations can affect flow control valve performance by influencing the pressure drop across the valve, potentially leading to variations in flow rate and reduced control accuracy.
Q: What are the considerations for selecting the sealing material for a flow control valve?
Considerations include the fluid properties, temperature range, compatibility with the valve and system materials, pressure rating, and the need for chemical resistance or tight shutoff capabilities.
Q: How can flow control valves be maintained for long-term reliability?
Flow control valves should be periodically inspected for leaks, wear, or damage, lubricated as recommended by the manufacturer, and undergo preventive maintenance tasks to ensure long-term reliability and performance.
You may also like
