Table of Contents
Brake System

Brake is one of most important device of a vehicle used for retarding or stopping the vehicle within smallest possible distance, in consistant with safety and without wheel skidding.
A brake is a mechanical device that inhibits motion by absorbing energy from a moving system.
The brakes also used to hold the vehicle at rest on an inclined road against the pull of gravity.
Need of Brake
1) The brakes must be strong enough to stop the vehicle within a short distance in an emergency but this should be consistent with safety. This is possible only when there is no wheel skidding and driver has proper control over the vehicle during emergency.
2) The brake must have good antifade characteristics i.e. the effectiveness of the brake should be remain constant with prolong application.
Principle of Braking System
1) The brakes works on the principle of friction.
2) The friction is basically the property of material in contact and depends upon the relative smoothness of the surface in contact.
3) In braking, two surfaces come in contact in motion which cause the kinetic energy to convert into heat energy due to friction.
4) The force of friction or retarding force created between the two mating surface ( brake lining and the brake drum ) depend upon the pressure or force exerted on the shoes.
5) The retarding force applied by the brake at the wheel depends upon the co-efficient of friction between the road and the tyre surface and the component of the weight on the wheel retarding force.
Type of Brakes
Mechanical Brake
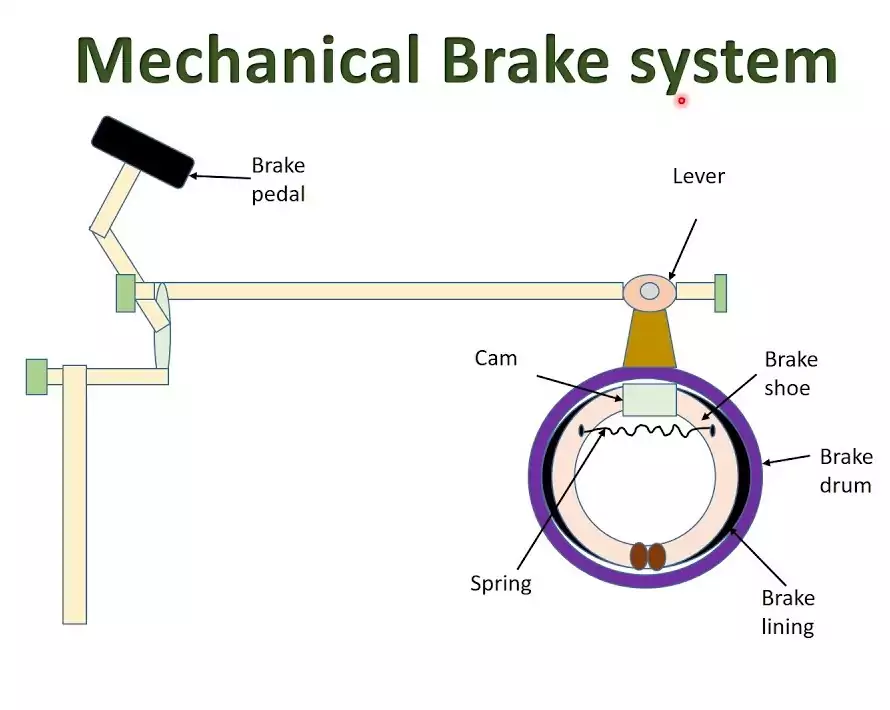
- Mechanical brakes are obsolete now as a service brake and these are still used on rear wheel in cars as a parking or emergency brake.
- The drum type manually operated mechanical brake system shown in fig. In a motor vehicle, the wheel is attached to the drum.
- The drum encloses the complete brake mechanism and protect it from dust and moisture. The inner side of drum is open. The backing plate at the open side of the brake drum completes the brake enclosure and hold the brake assembly.
- The backing plate is attached to the vehicle axle housing and acts as a base or frame for fastening the brake shoe and the operating cam mechanism with it linkage. The wheel attaching bolts on the brake drum connects the wheel and drum.
- The brake shoe are hinged to back plate at one end by an anchor join while other end rest on cam or toggle. This cam can be turn by camshaft which passes through hole in backing plate.
- The camshaft can be operated by brake padel through linkage. The brake shoe are pull inward or held by retracting spring.
- When brake pedal is pressed, the cam turn by the expanding brake shoe outward, against the retractor spring force.
- The brake lining comes in contact with brake drum causes friction between them.
- This force of friction opposes the direction of rotation and reduce the speed or stop the vehicle when brake pedal release, the retracting spring pull the brake shoe inward which turn the cam and brakes are release. This type of brakes are called internal expanding brake.
Hydraulic brake

- As compared to mechanical brakes, these brake system is silent, flexible and self lubricating. Also this system is highly efficient, durable and simple in design.
- The hydraulic braking system is based on pascal law which states that the fluid transmit pressure equally in all directions without any loss.
- This system is designed in such a way that even when brakes are in released position, a small pressure must be maintained in pipeline to protect the entering of air in the system when cup of wheel cylinder are kept expanded.
- This system consist of master cylinder, wheel clinder, steel pipe, flexible hose, brake linkage and a check valve at the end of master cylinder.
- When the operator presses the brake pedal, this force is transmitted to the piston in master cylinder through linkage.
- The piston in master cylinder moves by compressing the return spring. As bypass port is covered, further movement of piston builds up pressure in the compression chamber.
- When sufficient pressure is built up, the fluid checks the valve deflect and the fluid under pressure in the pipe line enters in wheel cylinder.
Brake | Definition, Need, Principle, Type, Working, An Overview
- As soon as the fluid enters in wheel cylinder, it exerts a pressure on two piston to move the piston outward. This outward motion of piston causes the brake shoe expand creating tension in retracting spring.
- The brake shoe lining is pressed tightly against the internal surface of brake drum. This friction between the brake lining and drum, slow down or stop the rotation of the drum and hence the vehicle slows down or stops.
- As brake pedal is released, the retracting spring pulls the brake shoe inward to original position. This causes the piston in wheel cylinder to push back. Due to this the brake fluid flows in reverse direction i.e. to the master cylinder and to fluid reservoir.
- As the pressure drops in the fluid line, the fluid checks valve at the end of master cylinder closes.
Pneumatic or Air Braking System
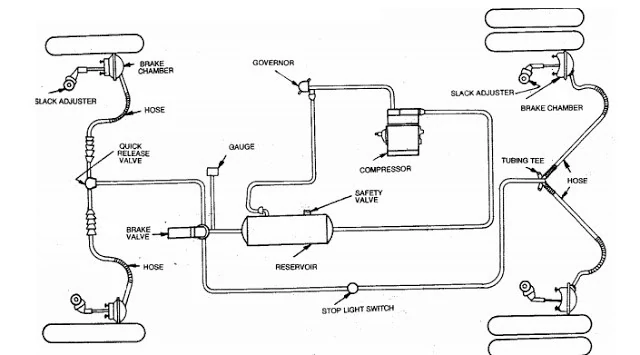
- Pneumatic braking system is used in medium and heavy duty vehicles.
- It consists of air filte, air compressor, unloader valve, reservoir, brake valve and brake chamber with steel tube and flexible hoses.
- The compressor is operated by engine. The compressor suck the air from atmosphere through air filter and compressed it to high pressure and discharge to the reservoir through oil separator.
- The pressure gauge is fitted to reservoir to indicated the pressure in the tank. The reservoir contain enough compressed air for several braking operation. The air from reservoir tank is supplied to brake valve and to other accessories.
- There is no braking effect until the brake pedal is not pressed as brake valve prevent the passege of air to the brake chamber.
- When brake pedal is pressed, the brake valve changes its position and brake valve open.
- The compressed air from brake valve flow to brake chamber acts on the flexible diaphragms in brake chamber.
Brake | Definition, Need, Principle, Type, Working, An Overview
- The diaphragm pushes the rods connected with the levers of brake gear cam. The cam turn and expend the brake shoe with make frictional contact with brake drum thus braking the wheels.
- When brake pedal is released, the supply of compressed air is cut off from the brake chamber and they are connected to atmosphere.
- The pressure from the chamber drops and brake shoes are returned to their initial position and wheel run free.
- The brake valve is equipped with servo-mechanism which ensure that the braking force on shoe proportional to the applied force on the pedal and also import relative reaction to the movement of the pedal. So driver can sense the degree of brake application.
- An unloader is located between the compressor and reservoir air pressure line. The unloader valve is relieves the compressor of its pumping load once the unloader the cut out pressure is obtained and seal the reservoir.
- When the compressure is built up a pressure depending upon the setting of the adjusting screw.
- The unloader then delivers the air discharge by the compressure to the atmosphere.Thus allowing the compressor to run light while the reservoir contain sufficient supply of air.
- The air filter prevent the dust and foreign material entering the operating system.These are mounted on the chassis and have a drain plug to allow the condensate to be easily removed.
Disc and Drum Brake

- In disc brakes friction surfaces are directly exposed to the cooling air while in drum type brake, the friction occurs on the internal surfaces, from which is dissipated only after it passed by conduction through the drum.
- In disc brake frictional pad are flat while in drum brake friction lining are curve shape.
- The design of disc brake is such that there is no loss of efficiency due to expansion. As in drum brake system became hot, expansion of a drum of internally friction surface apart, causing loss of effective pedal travel.
- On the other hand brake disc expansion merely changes the relative position on the friction surfaces slightly without tending to increase the clearance.
- Spot type disc brakes weightless than the conventional drum type counterpart a saving of approximately 20 % being possible.
- Disc brakes have better antifade characteristics than drum brake.
- The sensitivity of a brake to changes in the friction coefficient at the rubbing surfaces can be shown by plotting brake factor against friction coefficient.
- Total frictional area of pads in spot brake is very less compared to drum brake i.e. 1:4. This means the pressure intensity in disc brake is greater than drum type.
Brakes System Components
A vehicle’s braking system is a complex assembly of components working together to slow down or stop the vehicle.
The main components of a typical brake system include:
Brake Pedal
The brake pedal is the foot-operated lever inside the vehicle that the driver uses to activate the brakes.
Master Cylinder
The master cylinder is a hydraulic pump that converts the mechanical force applied to the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure. This pressure is then transmitted through the brake lines to the individual brakes.
Brake Lines
Brakes Lines are metal or flexible tubes that carry hydraulic fluid (brake fluid) from the master cylinder to the brake calipers or wheel cylinders at each wheel.
Brake Fluid
Fluid is a specially formulated hydraulic fluid that transmits the pressure from the master cylinder to the braking components. It is crucial for the proper functioning of the hydraulic brake system.
Brake Calipers (Disc Brakes) / Wheel Cylinders (Drum Brakes)
In disc brake systems, calipers contain pistons that press against brake pads, causing them to clamp onto the brake disc.
In drum brake systems, wheel cylinders push brake shoes against the brake drum, causing friction and slowing down the wheel.
Brake Pads (Disc Brakes) / Brake Shoes (Drum Brakes):
Brake pads are friction materials attached to the caliper in disc brake systems.
Brakes shoes are friction materials attached to the brake backing plate in drum brake systems.
These components make direct contact with the brake disc or drum, creating friction and slowing down the vehicle.
Brake Discs (Rotors) / Brake Drums
Brake discs, also known as rotors, are flat, disc-shaped components attached to the wheel hub in disc brake systems.
Brakes drums are cylindrical components attached to the wheel hub in drum brake systems.
These components provide the surface against which the brake pads or shoes create friction, leading to the vehicle’s deceleration.
Brake Booster
The brake booster is a device that assists in applying additional force to the master cylinder, making it easier for the driver to press the brake pedal.
Brake Proportioning Valve
This valve helps distribute hydraulic pressure between the front and rear brakes to ensure balanced braking performance.
Anti-lock Braking System (ABS)
The ABS is a safety feature that prevents wheel lock-up during hard braking. It includes sensors, control modules, and valves to modulate brake pressure.
Parking Brake (Handbrake)
The parking brake is a separate system that mechanically engages the brakes to keep the vehicle stationary when parked.
Understanding the function and condition of each of these components is essential for maintaining a vehicle’s braking system and ensuring safe operation. Regular inspections and timely replacements of worn-out parts are crucial for optimal brake performance and overall vehicle safety.
What are Brakes Pads?
Brake pads are a critical component of a disc brake system, which is one of the most common types of braking systems used in modern vehicles. The primary function of brake pads is to create friction and facilitate the slowing down or stopping of a vehicle.
Key features and functions of brake pads:
Location and Attachment:
Brake pads are typically located inside the brake calipers in a disc brake system.
They are attached to the caliper and positioned on both sides of the brake disc (rotor).
Friction Material:
Brake pads are made of a high-friction material that is designed to withstand high temperatures and provide effective stopping power.
Common materials used for brake pads include organic compounds, semi-metallic compounds, and ceramic materials.
Function:
When the driver presses the brake pedal, hydraulic pressure is applied to the brake caliper.
The caliper contains pistons that push the brake pads against both sides of the spinning brake disc.
The friction generated between the brake pads and the disc converts the kinetic energy of the rotating wheel into heat, slowing down the vehicle.
Heat Dissipation:
Brake pads must effectively dissipate heat generated during braking to prevent brake fade and maintain consistent performance.
The design and materials used in brake pads contribute to efficient heat dissipation.
Wear and Tear:
Brake pads undergo wear and tear during normal use, and their thickness gradually decreases over time.
Wear indicators, small metal tabs, are often integrated into brake pads. When the brake pads wear down to a certain point, these indicators make contact with the brake disc, producing a squealing sound to alert the driver that it’s time for replacement.
Types of Brake Pads
Organic Brake Pads: Made from a mixture of organic materials like rubber, carbon, and fiberglass. They provide good stopping power but may wear faster and generate more dust.
Semi-Metallic Brake Pads: Made from a blend of metal fibers, filler materials, and a binding resin. They offer excellent heat dissipation and durability.
Ceramic Brake Pads: Composed of ceramic materials and copper fibers. They are known for their low noise, low dust production, and good performance under various conditions.
Regular inspection and timely replacement of brake pads are essential for maintaining the effectiveness of the braking system and ensuring vehicle safety. Neglecting worn-out brake pads can lead to reduced braking performance and potential damage to other brake components.
What is a brake Inspection
A brake inspection is a thorough examination of a vehicle’s braking system to assess the condition and functionality of its components. Regular brake inspections are crucial for maintaining optimal brake performance, ensuring vehicle safety, and preventing potential issues that could compromise braking efficiency.
Key aspects of a typical brake inspection:
Visual Inspection
A visual examination of the brake components is the first step. This includes checking for visible signs of wear, damage, or brake fluid leaks.
Brake Fluid Check
The brake fluid level and condition are inspected. Brake fluid plays a crucial role in transmitting hydraulic pressure within the braking system, and it should be at the correct level and free from contamination.
Brake Pad and Shoe Inspection
The thickness and condition of the brake pads (in disc brake systems) and brake shoes (in drum brake systems) are assessed. Worn-out brake pads may need replacement to maintain optimal braking performance.
Brake Rotor and Drum Inspection
The condition of brake rotors (discs) and drums is examined. These components should be free from excessive wear, scoring, or grooving. In some cases, resurfacing or replacement may be necessary.
Caliper Inspection
The brake calipers are inspected for proper operation, leaks, and any signs of damage. Calipers should apply and release evenly to ensure even brake pad wear.
Brake Lines and Hoses
Brake lines and hoses are checked for signs of leaks, corrosion, or damage. Flexible hoses should be in good condition without cracks or bulges.
Brake Hardware Inspection
All associated hardware, such as clips, springs, and pins, is inspected to ensure proper function. Lubrication may be applied as needed.
Brake Pedal Feel
The brake pedal is tested for proper feel and responsiveness. A spongy or excessively firm pedal may indicate issues with the brake system.
Wheel Speed Sensor Check (ABS-equipped Vehicles)
If the vehicle is equipped with an Anti-lock Braking System (ABS), the wheel speed sensors are checked for proper operation.
Parking Brake Inspection
The parking brake is tested to ensure it engages and releases correctly.
Road Test
A road test may be conducted to assess the overall performance of the braking system, including pedal feel, noise, and any signs of vibration or pulling.
Based on the findings of the brake inspection, recommendations for maintenance or repairs may be provided. It’s important to follow the manufacturer’s recommended service intervals for brake inspections and to address any identified issues promptly to maintain the safety and reliability of the vehicle’s braking system.
Trouble shooting of Brakes
Troubleshooting brake issues is essential for maintaining vehicle safety.
Some common brake problems and their possible causes:
Spongy Brake Pedal
Possible Causes:
Air in the brake lines.
Brake fluid leak.
Worn brake pads or shoes.
Troubleshooting:
Bleed the brake system to remove air.
Inspect brake lines for leaks.
Check brake fluid level and top off if needed.
Inspect and replace worn brake pads or shoes.
Soft or Low Brake Pedal
Possible Causes:
Air in the brake lines.
Brake fluid leak.
Master cylinder issues.
Troubleshooting:
Bleed the brake system.
Inspect brake lines for leaks.
Check master cylinder for leaks and proper operation.
Brake Warning Light On
Possible Causes:
Low brake fluid.
Worn brake pads or shoes.
Brake system imbalance.
ABS system malfunction.
Troubleshooting:
Check brake fluid level and top off if needed.
Inspect brake pads or shoes for wear.
Check for ABS system trouble codes.
Inspect ABS sensors and components.
Brake Noise (Squeaking or Grinding)
Possible Causes:
Worn brake pads or shoes.
Glazed brake pads.
Foreign objects caught in the brake system.
Troubleshooting:
Inspect brake pads or shoes for wear.
Resurface or replace glazed brake pads.
Remove debris from the brake system.
Vibration or Pulsation During Braking:
Possible Causes:
Warped brake rotors.
Uneven brake pad wear.
Troubleshooting:
Inspect and resurface or replace warped brake rotors.
Ensure even wear of brake pads.
Brake Fluid Leaks
Possible Causes:
Damaged brake lines or hoses.
Leaking master cylinder.
Troubleshooting:
Inspect brake lines and hoses for leaks.
Check the master cylinder for leaks.
Pulling to One Side During Braking
Possible Causes:
Uneven tire pressure.
Uneven brake pad wear.
Brake caliper issues.
Troubleshooting:
Check and adjust tire pressure.
Inspect and address uneven brake pad wear.
Check brake calipers for proper operation.
ABS System Malfunction
Possible Causes:
Faulty wheel speed sensors.
ABS module issues.
Troubleshooting:
Retrieve and analyze ABS trouble codes.
Inspect wheel speed sensors and wiring.
Check ABS module for proper function.
FAQ’s
Why is it called a brake?
The term “brake,” as used in modern sheet metal manufacturing, comes from the Middle English verb breken, or to break, meaning to bend, change direction, or deflect. You could also “break” when you pulled the string of a bow to shoot an arrow.
When I brake, does my car stop?
First do a simple test. Apply the parking brake and, with the engine running, press the foot brake. If the engine turns off, it is a problem with the brake booster. If the engine continues to run with your foot on the brake, it is either a sensor problem or the idle speed is too low and the engine stalls.
Can you stop the car if the brakes fail?
Total brake failure
Use a manual parking brake (handbrake) in an on-off pumping motion, holding down the release button while doing this. If there is time, shift into second gear and gently lift the clutch (engine compression will make the clutch feel like a brake) and then use the handbrake to stop.
You may also like
