Table of Contents
Switched Mode Power Supply

A Switched-mode power supply (SMPS) is a type of electronic circuit that efficiently converts electrical power from one form to another.
It is used to convert a high voltage, low current AC input into a low voltage, high current DC output, typically used to power electronic devices such as computers, televisions, and other consumer electronics.
An SMPS uses a switching regulator to regulate the output voltage, which is much more efficient than a linear regulator, which dissipates excess power as heat. The switching regulator rapidly turns the power on and off, and adjusts the duty cycle to maintain a stable output voltage.
There are several types of SMPS, including the buck converter, boost converter, buck-boost converter, and flyback converter. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, and is used in different applications depending on the specific requirements of the device being powered.
SMPSs are commonly used in many different types of electronic devices due to their high efficiency, compact size, and low heat generation compared to traditional linear power supplies.
Basic operation of a switch mode power supply (SMPS)
A switch-mode power supply (SMPS) is a type of power supply that uses high-frequency switching to convert electrical power efficiently from one form to another. The basic operation of an SMPS can be summarized as follows:
AC voltage is first rectified into DC voltage using a diode bridge.
The DC voltage is then passed through a filter capacitor to smooth out the ripple and provide a steady DC voltage.
The DC voltage is then chopped into high-frequency pulses using a switching transistor or MOSFET.
These high-frequency pulses are then transformed by a high-frequency transformer to a different voltage level.
The transformed voltage is then rectified and filtered again to provide a stable output voltage.
The output voltage is then regulated using a feedback circuit that monitors the output voltage and adjusts the switching frequency to maintain a constant output voltage.
The high-frequency switching allows SMPS to be more efficient than linear power supplies because they waste less power as heat. SMPS are commonly used in applications where high efficiency and small size are important, such as in computers, televisions, and other electronic devices.
Switched Mode Power Supply components
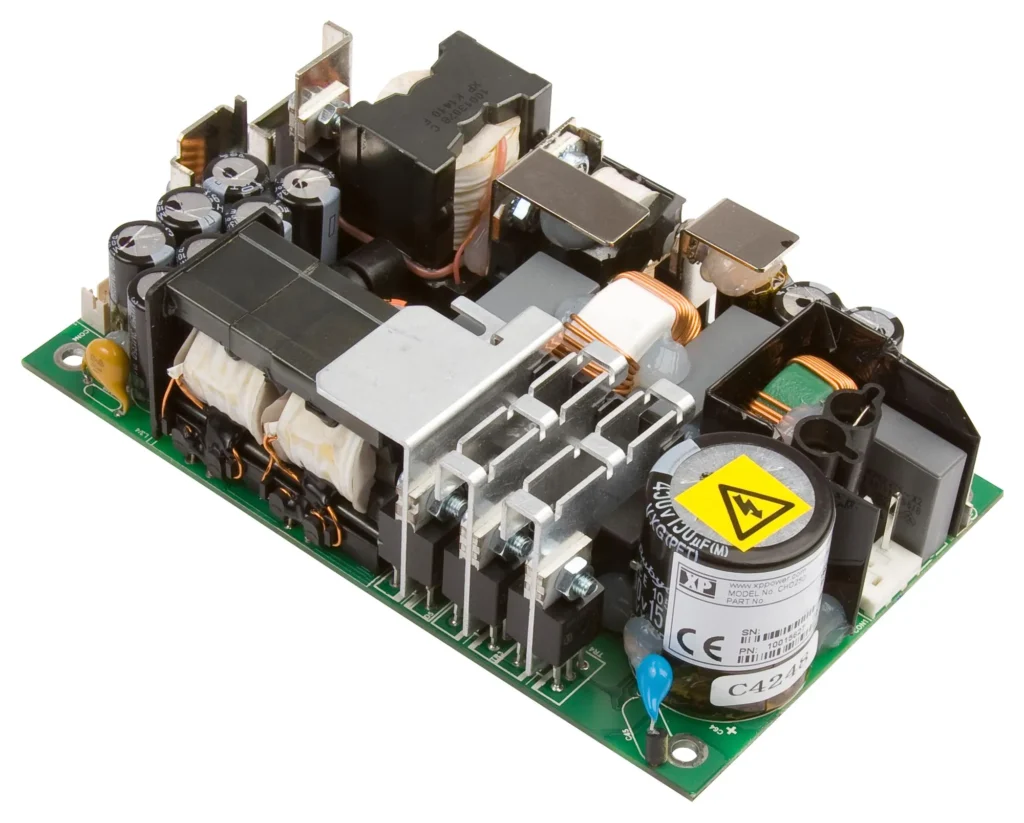
Switched-mode power supplies (SMPS) are complex electronic circuits that typically include the following components:
Input rectifier: Converts the incoming AC voltage to a pulsating DC voltage.
Filter capacitor: Smooths out the pulsating DC voltage from the input rectifier.
Power switch: Controls the flow of current to the output circuit.
Control circuit: Controls the power switch based on feedback from the output voltage and current.
Output rectifier: Converts the output voltage to DC.
Output filter: Smooths out the DC voltage and removes any remaining AC components.
Voltage output and current sensing circuit: Monitors the output voltage and current and sends feedback to the control circuit.
Protection circuit: Protects the SMPS from overvoltage, overcurrent, and other faults.
Transformer: Used to step down or step up the voltage.
Magnetic components: Inductors and transformers used to store and transfer energy.
Capacitors: Used for energy storage and filtering.
Diodes: Used for rectification and protection.
Resistors: Used for current sensing and voltage division.
Transistors: Used as switches and amplifiers.
Integrated circuits (ICs): Used for control and regulation.
These components work together to convert the input voltage to the desired output voltage and current with high efficiency and minimal losses.
The control circuit adjusts the power switch based on feedback from the output voltage and current to maintain the desired output voltage and regulate the output current.
The protection circuit ensures that the SMPS is protected from faults and overloads.
Types of switched-mode power supply Isolated converters
Switched-mode power supplies (SMPS) can be broadly categorized into two types: isolated and non-isolated.
Isolated SMPS have a transformer that electrically isolates the input and output circuits. This means that there is no direct electrical connection between the input and output, providing safety benefits in certain applications. Isolated SMPS can further be classified into different types:
Flyback converter: This is a simple and low-cost isolated SMPS that uses a transformer to store energy in its magnetic field during the ON period of the switching cycle, and then transfers the energy to the output during the OFF period.
Forward converter: This is another isolated SMPS that is similar to the flyback converter but uses a transformer with a center-tapped primary winding to transfer energy to the output.
Push-pull converter: This is a type of isolated SMPS that uses a transformer with a center-tapped primary winding and two switching transistors to transfer energy to the output.
Half-bridge converter: This is another type of isolated SMPS that uses a transformer with two equal primary windings and two switching transistors to transfer energy to the output.
Full-bridge converter: This is a more complex isolated SMPS that uses a transformer with four switching transistors to transfer energy to the output.
Each of these isolated SMPS types has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of the appropriate topology depends on the specific requirements of the application.
Non-isolated SMPS do not have a transformer, and therefore do not provide electrical isolation between the input and output circuits. Non-isolated SMPS can be simpler and less expensive than isolated SMPS, but may not be suitable for applications that require electrical isolation between input and output circuits.
Types of switched-mode power supply Non-isolated converters
Non-isolated switched-mode power supplies (SMPS) do not use a transformer to isolate the input and output circuits. Instead, they use capacitors or inductors to regulate the output voltage. Non-isolated SMPS can be further classified into different types:
Buck converter: This is a type of non-isolated SMPS that steps down the input voltage to a lower output voltage. It uses an inductor to store energy during the ON period of the switching cycle, and then transfers the energy to the output during the OFF period.
Boost converter: This is another type of non-isolated SMPS that steps up the input voltage to a higher output voltage. It uses a capacitor to store energy during the ON period of the switching cycle, and then transfers the energy to the output during the OFF period.
Buck-boost converter: This is a combination of the buck and boost converters, and can step down or step up the input voltage to a different output voltage.
Cuk converter: This is a type of non-isolated SMPS that can be used for voltage inversion, voltage reduction, or voltage increase. It uses two capacitors and an inductor to transfer energy between input and output.
SEPIC converter: This is another type of non-isolated SMPS that can be used for voltage inversion, voltage reduction, or voltage increase. It uses two capacitors and an inductor, and can regulate the output voltage even when the input voltage varies.
Non-isolated SMPS are often used in low-power applications, such as battery-powered devices and small electronic appliances. They are generally smaller and less expensive than isolated SMPS, but may not be suitable for applications that require electrical isolation between input and output circuits.
Switch mode power supply (SMPS) Principles

A switch-mode power supply (SMPS) is an electronic power supply that uses high-frequency switching to convert electrical power efficiently from one form to another. The principles of operation of an SMPS can be summarized as follows:
Rectification: AC voltage from the mains is rectified into DC voltage using a diode bridge. This process produces a pulsating DC voltage that needs to be smoothed out.
Filtering: The DC voltage is then passed through a filter capacitor to smooth out the ripple and provide a steady DC voltage.
Switching: The DC voltage is then chopped into high-frequency pulses using a switching transistor or MOSFET. The switching frequency can range from tens of kilohertz to several megahertz, depending on the application.
Transformation: These high-frequency pulses are then transformed by a high-frequency transformer to a different voltage level. The transformer can be used to step up or step down the voltage, depending on the application.
Rectification and Filtering: The transformed voltage is then rectified and filtered again to provide a stable output voltage.
Regulation: The output voltage is then regulated using a feedback circuit that monitors the output voltage and adjusts the switching frequency to maintain a constant output voltage. The feedback circuit can be either analog or digital, depending on the complexity of the application.
The high-frequency switching allows SMPS to be more efficient than linear power supplies because they waste less power as heat. SMPS are commonly used in applications where high efficiency and small size are important, such as in computers, televisions, and other electronic devices.
The type of SMPS used depends on the specific requirements of the application, and the choice of the appropriate topology depends on factors such as power output, efficiency, size, and cost.
Selection of an AC-DC SMPS
Selecting the right AC-DC switched-mode power supply (SMPS) can be a complex process, as it depends on several factors such as the input voltage range, output voltage and current, efficiency, reliability, and cost. Here are some steps to help you select the appropriate SMPS for your application:
Determine the input voltage range: Check the AC voltage range that your SMPS can handle. Some SMPS can only handle a specific input voltage range, while others can handle a wider range. Make sure that the input voltage range matches your specific application requirements.
Determine the output voltage and current: Determine the required output voltage and current for your application. Make sure that the SMPS you choose can provide the required output voltage and current without being overloaded.
Check the efficiency: Look for an SMPS with a high efficiency rating. A high-efficiency SMPS can save energy and reduce operating costs, especially if your application runs continuously.
Check the reliability: Look for an SMPS with a high reliability rating, especially if your application operates in harsh conditions. A reliable SMPS can reduce downtime and maintenance costs.
Consider the cost: SMPS prices can vary greatly depending on the power output, efficiency, reliability, and features. Make sure to consider the cost of the SMPS in relation to your application requirements.
Consider the form factor: Consider the size and form factor of the SMPS, especially if your application has space constraints.
Look for safety certifications: Make sure the SMPS you choose has appropriate safety certifications for your specific application. Look for certifications such as UL, CE, and RoHS.
Consider additional features: Some SMPS come with additional features such as overvoltage and overcurrent protection, thermal protection, and remote sensing. Consider these features based on your specific application requirements.
Advantages And Disadvantages
Switched-mode power supplies (SMPS) have several advantages and disadvantages compared to linear power supplies.
Some of the key advantages and disadvantages of SMPS
Advantages:
- Higher efficiency: SMPS are more efficient than linear power supplies, as they waste less power as heat. This efficiency results in lower power consumption and reduced operating costs.
- Smaller size and weight: SMPS are smaller and lighter than linear power supplies, making them ideal for applications where space is limited.
- Higher power density: SMPS can provide higher power density than linear power supplies, allowing for more power in a smaller package.
- Better voltage regulation: SMPS provide better voltage regulation than linear power supplies, as they can handle a wide range of input voltages and output voltages.
- Lower electromagnetic interference (EMI): SMPS generate less electromagnetic interference than linear power supplies, reducing the potential for interference with other electronic devices.
Disadvantages:
- Higher complexity: SMPS are more complex than linear power supplies, requiring more components and more advanced control circuitry.
- Higher cost: SMPS are generally more expensive than linear power supplies, especially for lower power applications.
- Potentially higher noise: SMPS can generate high-frequency noise, which can interfere with other electronic devices.
- Requires careful design: The design of an SMPS requires careful attention to detail, as the high-frequency switching can generate electrical noise and can be sensitive to component tolerances and layout.
- Potential reliability issues: SMPS can be more sensitive to voltage transients and spikes than linear power supplies, which can cause reliability issues if not properly protected.
SMPS have several advantages over linear power supplies, including higher efficiency, smaller size and weight, and better voltage regulation. However, they also have some disadvantages, including higher complexity and cost, potential noise and reliability issues, and the need for careful design.
Application of Switched Mode Power Supply (SMPS)
Switched Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) find widespread applications in various electronic devices and systems due to their efficiency, size, and weight advantages compared to traditional linear power supplies.
Some common applications of Switched Mode Power Supplies
Consumer Electronics:
Television and Monitors: SMPS are commonly used to power the electronics in TVs and computer monitors.
Audio Equipment: Many audio devices, such as amplifiers and speakers, utilize SMPS for power supply.
Computers and Servers:
Desktop Computers: SMPS are widely used in desktop computer power supplies due to their efficiency and compact size.
Servers and Data Centers: SMPS are employed to provide power to servers and data center equipment, where efficiency and space utilization are critical.
Telecommunications:
Routers and Switches: Networking equipment often relies on SMPS for power supply.
Mobile Phones: SMPS are used in chargers and power adapters for mobile devices.
Industrial Applications:
Automation Systems: SMPS are used to power various components in industrial automation systems.
Motor Drives: In applications where precise control of electric motors is required, SMPS can be used to provide power to motor drives.
Renewable Energy Systems:
Solar Power Inverters: SMPS are used in solar inverters to convert DC power generated by solar panels into AC power for use in homes and businesses.
Wind Power Converters: SMPS can be used in the power conversion and control systems of wind turbines.
Medical Equipment:
Imaging Systems: SMPS are utilized in medical imaging equipment such as MRI machines and X-ray systems.
Patient Monitoring Devices: Portable medical devices often use SMPS for power supply due to their compact size.
Aerospace and Defense:
Avionics: SMPS are used in aircraft for various avionic systems.
Military Applications: SMPS find applications in various military electronic systems and equipment.
LED Lighting:
LED Drivers: SMPS are commonly used as drivers for LED lighting systems due to their efficiency and ability to provide constant current.
Automotive Electronics:
Electric Vehicles (EVs): SMPS are used in the power electronics of electric vehicles for charging and motor control.
In-Car Electronics: Various electronic components in modern vehicles are powered by SMPS.
Power Banks and Chargers:
Portable Devices: SMPS are used in power banks and chargers for mobile devices to efficiently convert and regulate power from batteries.
FAQ
What is the function of an SMPS?
SMPS is an electronic power supply system that uses a switching regulator to effectively transfer electrical power.
Is SMPS AC or DC?
Switch Mode Power Supplies (SMPS), sometimes referred to as Switch Mode Power Supplies, have become the workhorse of efficient power conversion, taking a mains voltage AC input and converting it to an output low voltage DC.
What is SMPS voltage?
An SMPS can usually cope with a larger input variation before the output voltage changes. Universal or “wide input” power supplies, operating on mains voltages from 90 to 250 V, are common.
Is SMPS a transformer?
A switching power supply is an electronic power supply that incorporates a switching regulator to efficiently convert electrical power. On the other hand, Switch Mode Power Supply Transformers (SMPS) are a highly efficient form of transformer, which can be found in devices such as computer systems.
You may also like
