Table of Contents
Definition
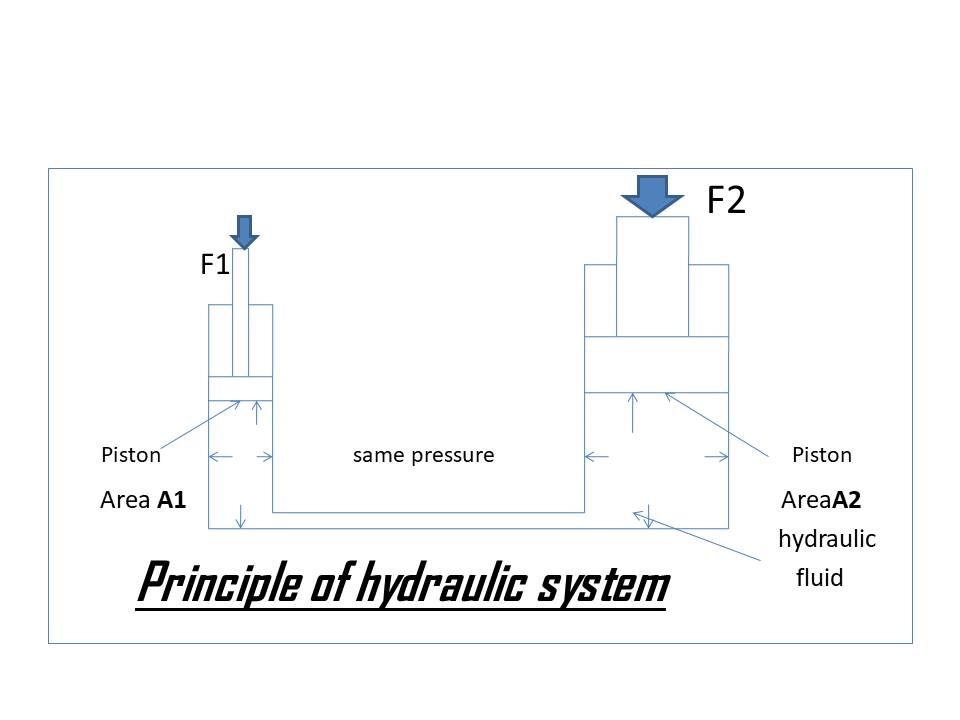
Hydraulic is the transmission and control of forces and motions through the medium of fluids. Oil hydraulic system operate on the principle of ‘Pascal Law’ and Pascal law says that –
” The pressure in a static hydraulic fluid in a closed system is same everywhere.”
Below fig. shows the use of Pascal’s law, which is useful for practical application of hydraulic system.
The Pascal’s law is very useful in designing of equipment’s and machines involved in hydraulic system. It is used in
- Hydraulic jack
- Hydraulic lift
- Crane
Hydraulic or fluid power system has wide spread applications in industry like
- Mechanical engineering
- Aircraft manufacturing
- Earthmoving equipment’s
- Agricultural equipment’s
Hydraulics refers to the science and technology of using fluids, typically liquids, to generate, control, and transmit power. It involves the use of pressurized fluid, usually oil or water, to perform various mechanical tasks.
In hydraulic systems, a fluid is used to transmit force or motion from one point to another.
The basic components of a hydraulic system
Hydraulic fluid: Typically, hydraulic oil is used as the working fluid in hydraulic systems. It is selected for its lubricating properties, resistance to degradation, and ability to handle high pressures.
Hydraulic pump: The hydraulic pump is responsible for generating flow and pressurizing the hydraulic fluid. It converts mechanical power, such as an electric motor or an engine’s rotational motion, into hydraulic power.
Hydraulic cylinder: Hydraulic cylinders, also known as actuators, are devices that convert hydraulic pressure into linear mechanical force. They consist of a cylindrical barrel, a piston, and a rod. When pressurized fluid enters the cylinder, it pushes or pulls the piston, resulting in linear motion.
Control valves: Control valves are used to regulate the flow and pressure of hydraulic fluid in the system. They direct the fluid to specific actuators or control the speed and direction of movement.
Hydraulic lines: Hydraulic lines or hoses carry the pressurized fluid from the pump to the actuators and back to the reservoir. They need to be designed and maintained to withstand high pressure and ensure leak-free operation.
Hydraulic reservoir: The hydraulic reservoir stores the hydraulic fluid and helps dissipate heat generated during operation. It also serves as a filter for contaminants in the fluid.
Type of Fluid Power System
Fluid power system is highly versatile power transmission system which utilizes energy of fluid to perform the task.
- Oil Hydraulic System
When pressurised oil is used as a working medium to perform the task, it is known as hydraulic system.
- Pneumatic System
When compressed air is used as a working medium to perform the task, it is known as pneumatic system.
Why are hydraulic systems used?
The main reason for using hydraulics is the high power density and secondly the simplicity coming from using few components to realize complex and fast moving machines with a high degree of safety.
Hydraulic system at main drive?
It is a transmission technology in which a fluid is used to move energy from pump to hydraulic cylinder. The fluid is incompressible and the fluid path can be flexible in the same way as an electrical cable.
Where it is used for?
They are mainly used when high power density is needed. This is especially the case in all types of mobile equipment such as excavators and in industrial systems such as presses.
It is used in hydraulic jack, crane, lift etc. Hydraulic system has wide spread applications throughout industry for e.g. mechanical engineering, aircraft manufacturing, ship building.
Important properties
The primary function of a hydraulic fluid is to convey power to the desired point of application. The efficient running of hydraulic system depends upon using the correct fluid and keeping the fluid in good condition.
1. Compressibility :- Liquids are incompressible in nature hence they are suitable for precise motion control. Hydraulic oil should have low compressibility for better performance.
2. Viscosity :- Oil with low viscosity flows easily but thick oil flows with some difficulty and results in pressure loss in the pipes and fittings.
3. Corrosion resistance :- The oil should have high corrosion resistance to eliminate the problems related to corrosion.
4. Pour point :- It is important during low temperature applications in cold climates. The oil should have low pour point temperature.
5. Demulsibility :- It means water separation, water that enters a hydraulic system can emulsify and causes collection of dust, grit and dirt and reduces operational efficiency. The resistance of a hydraulic fluid to emulsification or the ability of oil to resist with mixing with water is known as demulsibility.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Hydraulic
Advantages
1. No need of lubrication
2. Smooth working
3. Easy power distribution
4. Accuracy of motion
Disadvantages
1. Oil leakages problem
2. High maintenance cost
3. Disposal problem of uses oil
4. Dirty environment
Application of Hydraulic
Hydraulic systems are widely used in various industries and applications due to their ability to transmit power and control motion efficiently using fluids (typically oil) under pressure. Here are some common applications of hydraulic systems:
Heavy Machinery and Construction Equipment: Hydraulic systems are commonly found in heavy machinery such as excavators, bulldozers, cranes, and backhoes. They provide the necessary power to lift heavy loads, dig, and move earth and materials.
Aircraft: Hydraulic systems play a crucial role in the operation of aircraft. They are used to control landing gear, flaps, brakes, and other critical functions. Hydraulic power is reliable and can operate at high pressures, making it ideal for aviation applications.
Automotive: Hydraulic systems are used in vehicles for power steering, braking systems (hydraulic brakes), and automatic transmissions. Hydraulic power assists in steering and braking, making these operations easier for drivers.
Manufacturing and Industrial Machinery: Hydraulic systems are widely used in manufacturing processes, including presses, injection molding machines, and hydraulic cylinders used for lifting and clamping. They provide precise control over force and motion.
Mining: Hydraulic systems are integral to mining operations, powering equipment like rock drills, haul trucks, and shovels. They can handle the high forces and heavy loads encountered in mining environments.
Marine Industry: Hydraulic systems are used in ships and boats for various purposes, including steering systems, anchor handling, winches, and loading/unloading cargo.
Aerospace: In addition to aircraft, hydraulic systems are used in space exploration for tasks like deploying solar panels and manipulating robotic arms on spacecraft.
Material Handling: Hydraulic lifts and elevators are commonly used for lifting heavy loads in warehouses, factories, and buildings. They offer smooth and precise vertical motion.
Defense and Military: Hydraulic systems are used in military vehicles, tanks, and equipment for various functions, including turret rotation and weapon systems.
FAQ’s
What is a hydraulic system?
In a hydraulic system, the pressure applied to a fluid contained at any point is transmitted without decrease. That pressurized fluid acts on each part of the section of a containing vessel and creates force or power.
Why is hydraulics used?
Hydraulic systems are capable of moving heavier loads and providing greater force than mechanical, electrical or pneumatic systems. The fluid power system means it can easily cope with a wide range of weight without having to use heavy gears, pulleys or levers.
Who discovered hydraulics?
The history of hydraulics: from ancient times to the present
It is difficult to say exactly who invented hydraulics or when hydraulic systems were invented. Hydraulic systems have been created from the work of great minds such as Blaise Pascal, Joseph Bramah, Leonardo da Vinci and Galileo Galilei.
You may also like