Table of Contents
Reed switch
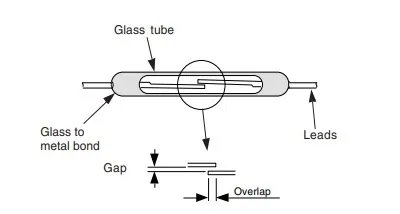
A Reed switch is a type of electrical switch that is activated by a magnetic field. It consists of two ferromagnetic reeds inside a glass tube, which are hermetically sealed and separated by a small gap. When a magnet is brought close to the switch, the magnetic field causes the reeds to come together, completing the electrical circuit.
Reed switches are commonly used in a variety of applications, such as in security systems to detect the opening of doors or windows, in level sensors to detect the level of liquids, in flow sensors to measure the flow of fluids, and in automotive systems to control lighting and other functions.
Reed switches have the advantage of being very reliable and durable, since they have no moving parts other than the reeds themselves. They are also very sensitive and can be used to detect very small magnetic fields. However, they do have some limitations, such as a relatively low maximum switching current and a limited number of switching cycles.
What is the working principle of reed switch?
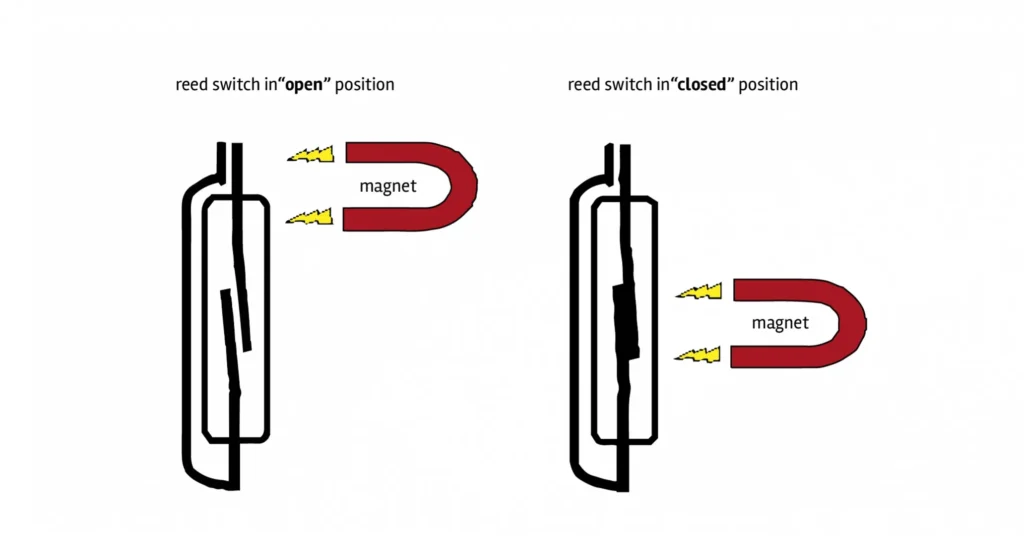
The working principle of a reed switch is based on the interaction between magnetic fields and the ferromagnetic material of the switch. A reed switch consists of two thin, flat ferromagnetic reeds, typically made of nickel-iron or a similar alloy, which are positioned in a hermetically sealed glass tube.
When no external magnetic field is present, the reeds are separated by a small air gap and the switch is open, meaning that no current can flow through it. However, when a magnetic field is applied to the switch, the ferromagnetic material of the reeds becomes magnetized and attracts each other, causing the reeds to come into contact and complete the electrical circuit. When the magnetic field is removed, the reeds return to their original position and the switch opens again.
The sensitivity of a reed switch depends on the strength of the magnetic field, the distance between the magnet and the switch, and the orientation of the magnetic field with respect to the reeds. Reed switches are typically used in applications where they are triggered by the proximity of a permanent magnet, an electromagnet or a magnetic field produced by a moving object.
How reed switch work?
Reed switches work on the principle of magnetism. They consist of two ferromagnetic reeds inside a glass tube, which are hermetically sealed and separated by a small gap. When a magnetic field is applied to the switch, the ferromagnetic material of the reeds becomes magnetized and attracts each other, causing the reeds to come into contact and complete the electrical circuit.
When no external magnetic field is present, the reeds are separated by a small air gap, and the switch is open, meaning that no current can flow through it. However, when a magnetic field is brought close to the switch, it causes the reeds to come together, completing the electrical circuit. When the magnetic field is removed, the reeds return to their original position, and the switch opens again, breaking the circuit.
Reed switches are widely used in various applications, such as in security systems to detect the opening of doors or windows, in level sensors to detect the level of liquids, in flow sensors to measure the flow of fluids, and in automotive systems to control lighting and other functions. They have the advantage of being very reliable and durable, since they have no moving parts other than the reeds themselves.
Type of reed switch
There are several different types of reed switches, including normally open (NO) reed switches, normally closed (NC) reed switches, and changeover reed switches. Normally open reed switches are open when no magnetic field is present, and close when a magnetic field is applied. Normally closed reed switches are the opposite – they are closed when no magnetic field is present, and open when a magnetic field is applied. Changeover reed switches have both a normally open and normally closed contact.
Reed switches can also be classified by their size, sensitivity, and power rating. Some common types of reed switches include miniature reed switches, high power reed switches, and surface mount reed switches.
Advantages and Disadvantages of reed switch
Advantages
Reliable: Reed switches are very reliable and durable, as they have no moving parts other than the reeds themselves.
Low Power Consumption: Reed switches are very efficient and consume very little power.
Simple Operation: Reed switches are simple to use and operate, requiring only the presence or absence of a magnetic field to turn them on or off.
Compact Size: Reed switches are compact in size and can be easily incorporated into small devices or systems.
Fast Response Time: Reed switches have a fast response time and can detect changes in magnetic fields almost instantly.
Disadvantages
Limited Switching Cycles: Reed switches have a limited number of switching cycles, typically around 10 million cycles, after which the switch may fail.
Limited Current Handling: Reed switches are typically limited to switching low current loads and may not be suitable for high-power applications.
Sensitivity to Magnetic Fields: Reed switches are highly sensitive to magnetic fields, and may be triggered by stray magnetic fields, which could result in false triggering.
Fragility: Reed switches are relatively fragile and can be easily damaged if they are subjected to shock or vibration.
Limited Operating Temperature: Reed switches have limited operating temperatures, and extreme temperatures can cause the reed switch to malfunction.
Application
Reed switches have many applications in various industries. Some common uses of reed switches include:
Security Systems: Reed switches are commonly used in security systems to detect the opening of doors or windows. When the door or window is opened, the magnetic field is disturbed, triggering the reed switch and activating an alarm.
Proximity Sensors: Reed switches can be used as proximity sensors to detect the presence or absence of a magnetic field. They are commonly used in industrial applications to detect the position of moving objects or to detect the presence of metallic objects.
Level Sensors: Reed switches can be used in level sensors to detect the level of liquids in tanks or reservoirs. When a float with a magnet attached to it moves up or down with the liquid level, it triggers the reed switch, indicating the level of the liquid.
Flow Sensors: Reed switches can be used in flow sensors to measure the flow of fluids. They are commonly used in water meters to detect the flow of water through a pipe.
Automotive Applications: Reed switches are used in automotive applications to control lighting and other functions. For example, they are used in car door switches to turn on interior lights when the door is opened.
Medical Devices: Reed switches are used in some medical devices, such as implantable devices, to detect the presence of a magnetic field and trigger a response.
Consumer Electronics: Reed switches can be used in consumer electronics devices, such as smartphones, to detect the presence of a magnetic cover and turn the device on or off.
Reed switches are widely used in many applications due to their simplicity, reliability, and efficiency.
FAQ
What does a reed switch sensor do?
Reed sensors make it easy to open and close automatic doors.
What is a reed switch example?
Magnet-actuated reed switches are commonly used in mechanical systems as proximity sensors. Some examples are door and window sensors in burglar alarm systems and tamper protection methods.
What size is a reed switch?
Over the years, the reed switch size has shrunk from about 50 mm (2 inches) to 3.9 mm (0.153 inches) or less.
How far away does the reed switch detect?
Proximity Reed switch BN 32
actuating magnet, the BN 32 magnetic reed switch is capable of actuating distances of up to 55 mm.
You may also like
